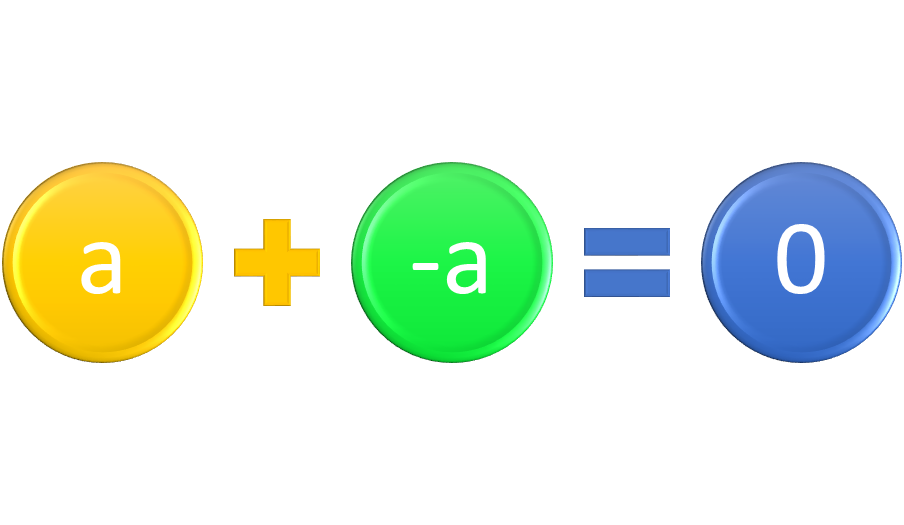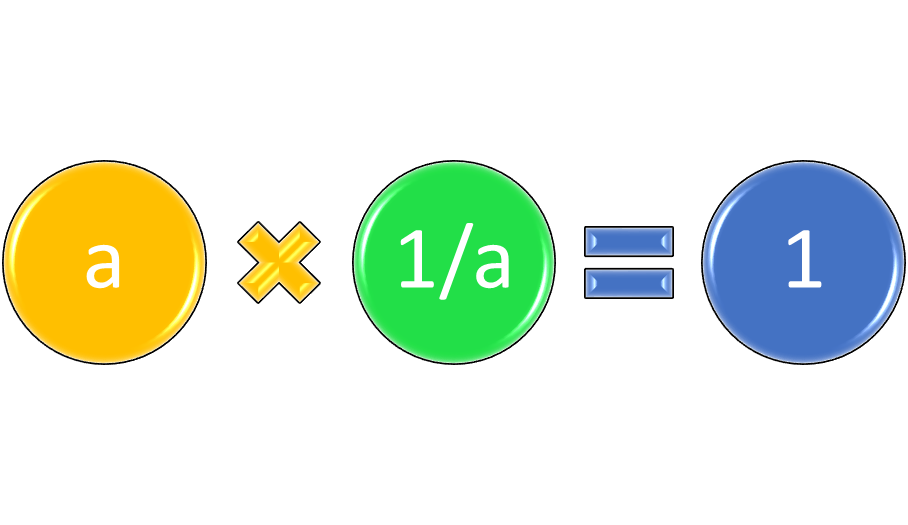Overview
Real numbers are numbers on the number line. This includes positive and negative numbers, integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, and the number zero. Real numbers have certain mathematical properties, including commutative, associative, distributive, identity, and inverse properties.
Commutative Properties
The commutative properties hold for addition and multiplication of real numbers. In symbol form, the Commutative Property for Addition is stated as a + b = b + a. For example, 2 + 4 = 4 + 2. Also, 3 + -4 = -4 + 3. The Commutative Property for Multiplication in symbol form is a∙b = b∙a. For example, 5 ∙ 7 is the same thing as 7 ∙ 5. The commutative property does not hold for subtraction or division. In symbol form, a-b is not the same thing as b-a. For example, 5-3 = 2, but 3-5 = -2, not the same. Also, a/b is not the same thing as b/a. For example, 5/20 equals 1/4, but 20/5 equals 4.
Figure 1: The Commutative Properties for Addition and Multiplication.
Associative Properties
The Associative Property of Addition states that for any real numbers a, b, and c, (a + b) + c = a + (b + c). For example, (5 + 6) + 7 equals 11 + 7 or 18. 5 + (6 +7) equals 5 + 13, which also equals 18. The groups of numbers have just changed. The Associative Property of Multiplication states that for any real numbers a, b, and c, (a ∙ b) ∙ c = a ∙ (b ∙ c). For example, (3∙ 2) ∙ 5 equals 6∙ 5, or 30, and 3 ∙ (2∙5) equals 3∙ 10, or 30.
Figure 2: The Associative Properties for Addition and Multiplication.
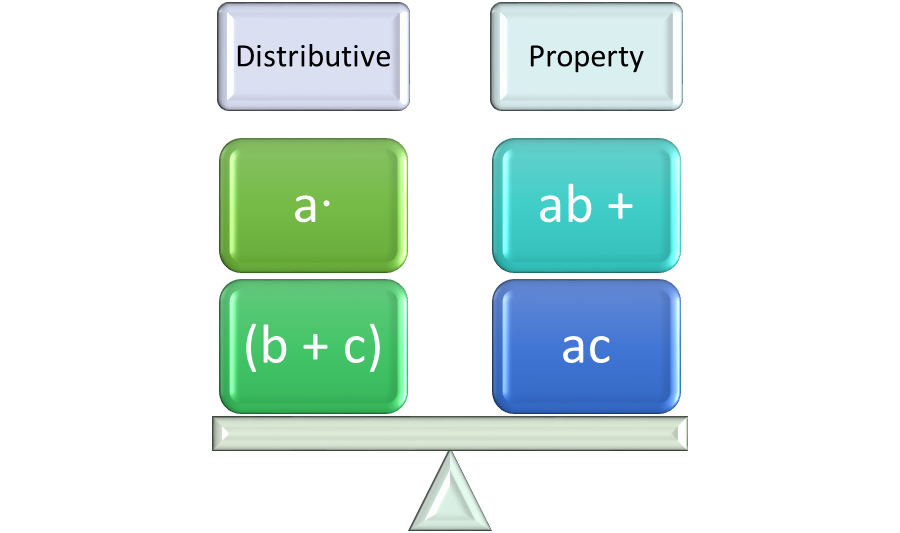
Distributive Property
The Distributive Property involves 2 operations, multiplication and addition. In symbol form, a (b + c) = a∙b + a∙ c. For example, 5(2 + 2) = 20, and so does 10 + 10. There is also a Distributive Property of Multiplication over Subtraction such that a ∙ (b-c) = a∙ b –a ∙c. For example, 7 ∙ (5 -2) = 21, and so does 35 – 14.
Figure 3: The Distributive Property distributes multiplication over addition (or subtraction).
Identity and Inverse Properties
The identity element for addition is 0. Any real number plus 0 equals the number. The identity element for multiplication is 1. Any real number times 1 equals the number. The additive inverse for any real number a is –a, and a + -a = 0, the identity element for addition. The multiplicative inverse for a, a not equal to 0, is its reciprocal, 1/a. In symbol form, a ∙ 1/a = 1, the identity element for multiplication.
Figure 4: Adding a real number and its additive inverse = 0, the additive identity, and multiplying a real number times its multiplicative inverse = 1, the multiplicative identity.
Interested in algebra tutoring services? Learn more about how we are assisting thousands of students each academic year.
SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. We offer tutoring programs for students in K-12, AP classes, and college. To learn more about how we help parents and students in Coral Springs, FL: visit Tutoring in Coral Springs, FL