Overview
The sport of soccer is popular worldwide. Like other sports, the ball and the players follow laws of physics as games are played, especially Newton’s Laws of Motion, friction, momentum, and aerodynamics.
Laws of Motion
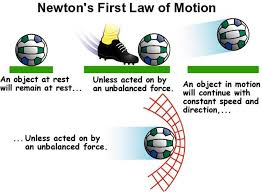
Newton’s First Law
According to Newton’s First Law of Motion, a soccer ball will stay at rest unless a force of some sort moves it, and it will stay in motion unless a different force stops it. The force that usually moves the soccer ball is the player’s kick. Another player blocks its motion. The game would be very boring if the eleven players of one team and the eleven players of the opposing team stood on opposite sides of the field and the ball stayed at rest.
Newton’s Second Law
According to Newton’s Second Law, the force behind the soccer ball equals its mass times acceleration, in the equation F =ma. A hard kick will move the soccer ball farther and faster than a soft kick. The acceleration of the ball depends upon how much force behind the kick.
Newton’s Third Law
According to Newton’s Third Law, for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. The player kicks the soccer ball, and the ball “kicks” back, but the player doesn’t feel the reaction because the player’s leg has more mass and force than the soccer ball.
Friction
The soccer ball doesn’t continue to move indefinitely because of friction between the ball and the grass as it bounces across the field. Players use friction to slow the motion of the ball, as a way to control it and keep it from going out of bounds. When the ball is kicked off-center, the friction between the air and the ball creates curvature of motion.
Momentum
The players are constantly in motion, and transfer momentum to the ball by the motion of their feet, so that the ball goes in the direction they want. They can kick the ball in such a way to spin it, making it harder for opposing players to stop its motion. Players can use the momentum of the ball to control its motion.
Aerodynamics
A soccer ball is a sphere that has less resistance and drag from its motion through the air. Its center of gravity is in the center of the ball. The official World Cup soccer ball looks somewhat different than the typical polygon-tiled soccer ball. The panels are joined with deeper seams and covered with tiny bumps to maximize the airflow, so it can go faster and straighter.
Interested in science tutoring services? Learn more about how we are assisting thousands of students each academic year.
SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. We offer tutoring programs for students in K-12, AP classes, and college. To learn more about how we help parents and students in Cumberland, MD: visit Tutoring in Cumberland, MD