Overview
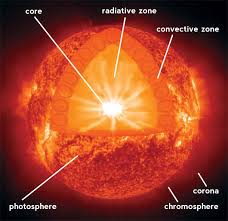
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is 149,600,000 km from Earth, and generates its own energy. At its core, nuclear fusion converts hydrogen to helium. Vast amounts of energy radiate outward to the surface. The Sun is surrounded by an atmospheric layer that includes the corona.
The Nuclear Core
The Sun itself is a sphere of hot plasma with a diameter about 109 times that of Earth. Its mass is about 330,000 times that of Earth. When the Solar System formed over 4.5 billion years ago, the disk of protostellar matter collapsed in the center from its own gravity. It heated enough to fuse hydrogen atoms into helium. It is about 15.7 million degrees Celsius at the core, so hot that protons are free to react with one another.
Radiation and Convection
The core is only about 20% of the mass of the Sun. Energy from nuclear fusion radiates outward in the form of intense gamma rays in a zone to about 70% of its mass. As it radiates, thermal columns carry heat to the surface. Solar matter rises and sinks in continuous convection currents.
The Photosphere
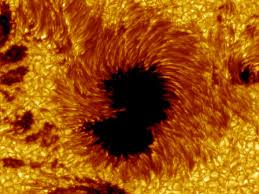
The photosphere is the surface of the Sun where light is visible. Its temperature is between 4230 and 5730 °C, and it is not solid. Matter forms cells of plasma called granules that rise and fall with convection currents of their own. Sunspots are cooler areas that appear darker than the surrounding plasma, although they are actually between 2700° and 4200° C. They can be anywhere from 16 km to 160,000 km in diameter, and usually occur in pairs or groups.
The Solar Atmosphere
The solar atmosphere is above the photosphere, and is divided into zones. The chromosphere is much less dense than the atmosphere of Earth. The corona and chromosphere are most usually visible during a solar eclipse. Its temperature is higher than the surface of the Sun, and consists of many active filaments of very hot plasma. Many of its dynamic features were observed from suborbital telescopes launched in 2012 and 2013. The solar wind consists of plasma that escapes the Sun’s gravity. It can be detected as far away as beyond the orbit of Pluto.
Interested in science tutoring services? Learn more about how we are assisting thousands of students each academic year.
SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. We offer tutoring programs for students in K-12, AP classes, and college. To learn more about how we help parents and students in Valley City, ND: visit Tutoring in Valley City, ND