Overview
When hydrogen fuel is exhausted within a stellar core, rapid changes take place within the star depending upon its mass and temperature. Some of these nuclear reactions result in a stellar explosion and collapse. As all nuclear fuel is exhausted, matter is compressed into white dwarfs, black holes, and other cosmic variations.
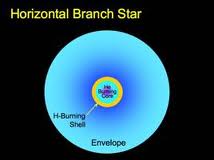
Structure of Helium-Burning Stars
Helium is heavier than hydrogen, so the core of a star becomes very dense. Eventually, many stars the mass of the sun have such dense, tightly packed cores that electrons are captured. In order to blow away the electrons, helium is ignited in a flash. The temperature becomes high enough that the helium atoms start the triple alpha process. The rest of the star that surrounds the core swells into cooler layers that are heated by convection. If the star is massive, it will explode as a supernova.
Planetary Nebula
The gaseous envelope that surrounds the helium-burning core thins as the star swells, and is driven away by strong stellar winds that are set up by convection. The process is theorized to last about 10, 000 years or so. The astronomer William Herschel observed nebulae that surrounded tiny stars, and thought the gases were condensing into far-away planets, so he named them “planetary nebulae.” Although any planets orbiting a helium core were probably vaporized in the stellar wind, the name stuck.
White Dwarfs
White dwarfs are stars that are so compact that a mass the size of the sun will be squeezed into a dense, white-hot ball the size of the earth. The matter contained in a white dwarf consists of degenerate electrons, protons, and neutrons. A teaspoon of white dwarf matter would weigh tons. Theories to explain white dwarfs come from quantum mechanics.
Black Holes and Variations
Heavier white dwarf stars are hotter, larger, and even more compact. Stars from about 1.4 times the mass of the Sun and 3 times the mass of the Sun are composed of neutrons. Their surface is mostly made of iron. They spin rapidly and become pulsars. Neutron stars are strong sources of radio waves. As the star cools, matter becomes so dense that it forms a black hole. No energy can escape the gravitational field of a black hole, called the event horizon.
Interested in science tutoring services? Learn more about how we are assisting thousands of students each academic year.
SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. We offer tutoring programs for students in K-12, AP classes, and college. To learn more about how we help parents and students in Lawrence, KS: visit: Tutoring in Lawrence, KS