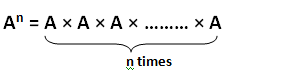The exponent of a number tells how many times the number is to be multiplied by itself. Exponent is more commonly called as power or index.
In general,
where,
– A is base
– n is exponent (or power, or index)
In word An could be called as A to the power b.
Example 1: 62 = 6 × 6 = 36
62 could be called as ‘6 to the power 3’, ‘6 to the second power’ or ‘6 squared’.
Example 2: 23 = 2 × 2 × 2 = 8
23 could be called as ‘2 to the power of 3, ‘2 to the third power’ or ‘2 cubed’
Example 3: 54 = 5 × 5 × 5 × 5
54 could be called as ‘5 to the power of 4’, ‘5 to the fourth power’ or ‘ 5 to the 4th’
Negative Exponent
The negative exponent is opposite of positive exponent. It can be solved in either of the two ways:
Method 1: First calculate An and then take the reciprocal.
For example, 5-3
5 × 5 × 5 = 125
So, 5-3 = 1/125
Method 2: First take the reciprocal and then calculate An.
For example, 7-2
7-2 = 1 ÷ 7-2 = 1/72
= 1/(7 × 7) = 1/49
Special case: Any number to the power of zero is 1.
i.e A0 = 1