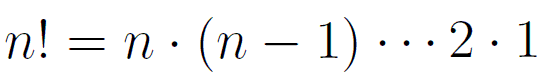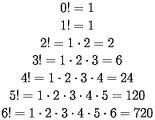Overview:
Factorials involve all possible outcomes of an event. They are calculated by multiplying the number of possible events times the number of events minus 1 times the number of events minus 2 until there is only one possibility left.
|
Figure 1: The factorial formula in mathematical symbols |
Example of a Factorial:
Suppose four actresses are chosen for a picture: Amy Adams, Charlize Theron, Halle Berry, and Jennifer Lawrence. Obviously, all four cannot have their names first on the billing, but there are four possibilities for the first billing to be chosen. For the second billing, there are only three possibilities, as the first one was chosen. For the third billing, there are only two possibilities, and for the fourth, there is only one. In this case, the multiplication 4∙3∙2∙1 is read as 4! (4 factorial). There are 24 different outcomes for the billing.
|
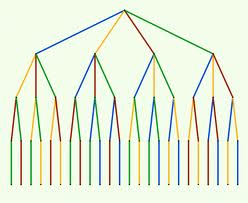
Figure 2: The factorial 4! Showing 24 different outcomes |
Permutations:
Permutations are one of the applications for factorials. They are rankings where the order matters, as in the example of the order of star billing. Suppose a music producer is choosing the order of songs on a CD released from a new artist. Only one song can be in each track. If there are 10 songs that have been recorded, there are 10 possibilities for the opening track. Since one song has already been chosen, there are 9 left for the second track. For the third track, there are 8 left, and so on, until the last song remains. The way to calculate the number of permutations is 10∙9∙8∙7∙6∙5∙4∙3∙2∙1 = 3, 628, 800. It would be difficult to list all of those permutations, but not impossible. If there are only 3 events to choose from, there are only 3∙2∙1 or 6 possible combinations.
|
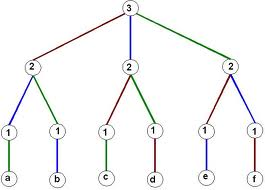
Figure 3: An example of permutations if there are only 3 possibilities. |
Factorial Identity and More:
The factorial 0! is defined as 1 for many of the same reasons that n0 is equal to 1. The factorial 1! follows the same pattern, of 1 multiplied only one time. The other factorials grow rapidly, as can be seen by the diagram.
|
Figure 4: The value of factorials. |
Choosing a Few Options:
Many times, all the possible permutations for all members in a system are not necessary. Suppose the task is just to place the first three runners in a race of 11 runners. All 11 participants have the possibility of getting first place, 10 participants have the possibility of getting second place, and 9 have the possibility of getting third place. There are 990 possible combinations of winners, or 11∙10∙9, compared to the entire possibility of 39,916,800 combinations down to 11th place.
Interested in algebra tutoring services? Learn more about how we are assisting thousands of students each academic year.
SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. We offer tutoring programs for students in K-12, AP classes, and college. To learn more about how we help parents and students in Sparks, NV visit: Tutoring in Sparks, NV