Overview
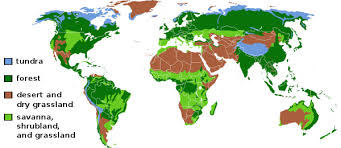
Biomes are environments that usually have similar climate, physical conditions, and broad general features. Similar organisms tend to gather in areas where they can thrive, because the climate and geographic location support comparable populations of plants and animals.
Tropical Biomes
Some types of tropical biomes include tropical rain forests, tropical dry forests, and tropical savanna, located in equatorial Africa, Southeast Asia, India, South and Central America, and in Australia. Those regions differ by the amount of rainfall they get, as well as the range of average temperature throughout the year. For example, rain forests in the tropics are hot and wet throughout the year. The moist, hot climate produces dense forests and jungles, home to many different plant and animal species from tall trees that form a canopy to large vines and leafy ferns. Tropical dry forests have wet seasons and dry seasons, but they are still warm year round. Tropical savannas are home to tall grasses and shrubs, large predators such as lions and cheetahs, and herds of zebras and giraffes, if the land is left undisturbed. Deserts are found in tropical parts of the world as well as other climates. Although they receive less than 25 cm of rainfall per year, they support varied life-forms from cacti, mountain lions, reptiles such as rattlesnakes and lizards, as well as various types of insects that live in dry climates such as scorpions.
Temperate Biomes
Temperate biomes include temperate grassland, as well as temperate woodland and shrub land. Temperate grassland areas include the Great Plains of the Midwestern United State, large areas of central Asia and central Europe, and plateaus of South America. The land is very fertile, and grasses are denser than those in tropical savannas, because the soil is richer in nutrients. Temperate woodland and shrub land are mixed, especially in higher elevations.
Forests
Forests in temperate regions grow a mixture of deciduous trees, that shed their leaves in autumn, and evergreen trees that do not shed their leaves. Many different types of plants and flowers grow in the spring. Animals such as deer, black bears, squirrels, and raccoons live in temperate forests. Temperate forests from the Pacific coast of northern California, through Washington, Oregon, western Canada, and Alaska have many different types of conifers, or cone-bearing evergreen trees such as cedar, hemlock, and fir. The northernmost forests of North America, Asia, and northern Europe are called taiga. Winters are bitterly cold, but the ground thaws in the summer.
Tundra, Mountain Peaks, and Polar Ice Caps
The subsoil remains permanently frozen in the northernmost tundra. Plants such as lichen grow close to the ground, and animals such as caribou, musk, ox, and Arctic foxes live under harsh conditions. Biomes in and around mountains vary with elevation, so that grassy foothills and meadows are replaced by forests, relatively barren areas above the tree line, and ice fields. The polar ice caps are cold year round, and are home to very few plants and animals.
Interested in science tutoring services? Learn more about how we are assisting thousands of students each academic year.
SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. We offer tutoring programs for students in K-12, AP classes, and college. To learn more about how we help parents and students in Winnipeg, MB: visit Tutoring in Winnipeg, MB