Overview
Human activity has affected the biosphere on Earth as the population has grown to over 7 billion. Some of the most troubling effects include changes to the ozone layer and global warming.
The Stratosphere
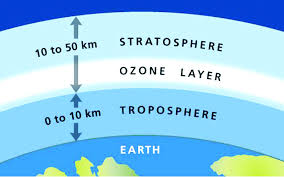
The stratosphere in Earth’s atmosphere is between 10 and 50 km above the surface. It has an inverted temperature, so that the warmer layers are higher up and the cooler layers are closer to the troposphere. The temperature inversion is caused by chemical reactions as ozone (O3) absorbs ultraviolet radiation from the Sun, releasing energy and oxygen molecules. At the higher levels of the stratosphere, more ultraviolet radiation warms the atmosphere than at the lowest levels.
The Ozone Layer
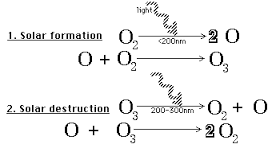
The ozone layer contains the highest concentration of ozone in the atmosphere, although that is still less than 10 parts per million. Oxygen generally exists in the atmosphere as molecules of 2 oxygen atoms bound together as O2. When ultraviolet light strikes the oxygen molecule, it breaks its bonds. Sometimes free oxygen combines with an oxygen molecule to form ozone. The chemical reactions between ultraviolet light and ozone screen out 97-99% of the most harmful ultraviolet rays from reaching the surface and destroying life. Intense ultraviolet rays can cause sunburn, cancer, damage to the eyes, as well as damaging plant tissue and plankton.
The Ozone Hole
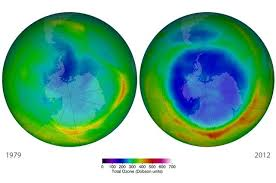
The ozone layer has been studied extensively, because of its role in protecting life on Earth. In the 1970s, scientists noticed a gap in the ozone layer over Antarctica. It has grown larger, and there is also a thinning layer over the Arctic pole. Scientists have determined that the thinning ozone layer is caused largely by propellants and pollution by a class of chemicals called CFC’s. Many countries around the world have joined together to ban the use of those chemicals.
Global Warming
Global warming is a much more controversial problem. The average temperature of the entire planet has been increasing over the past 100 years, with the greatest increase occurring in the last 20-30 years. Greenhouse gases trap heat at a greater rate than it is radiated away from the Earth, as they both absorb and give off infrared radiation, while other compounds in the atmosphere do not.
Causes of Global Warming
Scientists believe that the rise in greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, nitrous oxide, and ozone) is due to a number of factors that increase pollution and precipitate chemical reactions in the atmosphere. Some of these include the exhaust from the burning of fossil fuels and other carbon-based fuels, and extensive clearing of forests. Volcanic eruptions and natural changes in water temperature also can contribute to global warming, but most of the rise in greenhouse gases is due to human activity.
Effects of Global Warming
Increased temperature, especially in the Arctic, melts ice caps, glaciers, and permafrost, resulting in habitat changes for many species of plants and animals. Also, extreme weather, such as increased rainfall in some areas, droughts in others, and heat waves, affects the growth of food crops and other plants. Although scientists and politicians do not always agree on the best course of action to slow global warming, many agree that changes need to be made.
Interested in science tutoring services? Learn more about how we are assisting thousands of students each academic year.
SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. We offer tutoring programs for students in K-12, AP classes, and college. To learn more about how we help parents and students in Hilo, HI: visit Tutoring in Hilo, HI