Overview
Seed plants have three main parts that serve specialized functions: roots, stems, and leaves. Roots help to anchor the plant in the ground as well as absorbing water and nutrients from the soil. Stems support the part of the plant that lies above ground and transport water and nutrients to all parts of the plant. Leaves carry out photosynthesis, which is the most important way that plants produce the energy to live.
Specialized Tissues in Plants
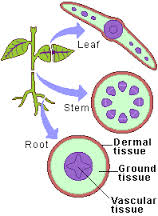
Plants have tissue systems that are specialized for functions such as growth, regulating water and protecting against injury, transporting water and other nutrients to all parts of the plant, as well as cells that form the supporting structure of the plant. Plants grow from specialized cells at the tips of shoots and roots. Dermal tissue forms the outer covering of the plant, along the stems, the leaves and the roots. The thin outer covering helps to keep the plant from drying out and protects the inner parts of the plant against injury. The cells that are specialized for vascular tissue form hollow tubes throughout the plant to carry water and other nutrients throughout the plant. Some types of ground tissues have thick cell walls to form structures that support the plant, and other types are contained in leaves to carry out photosynthesis.
Figure 1: Diagram of a plant showing parts and specialized tissues.
Roots
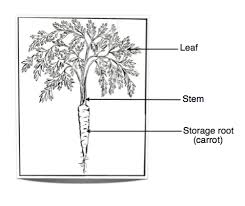
There are two main types of roots, taproots and fibrous roots. Some taproots, such as those of trees, extend very deep towards water, while others store sugars and starches. Root vegetables such as carrots, beets, and radishes are edible taproots. Grasses and similar plants have fibrous roots that branch and form networks that keep soil from eroding. Roots absorb water and nutrients from soil.
Figure 2: Root vegetables such as carrots have edible taproots.
Stems
Stems produce leaves, branches, and flowers. They hold the leaves up to the sunlight so they can carry out photosynthesis. They transport water and nutrients between the roots to the leaves, and they also give structure to the plant. The stems of trees have very complex patterns of woody stems that grow thicker as the trees grow.
Leaves
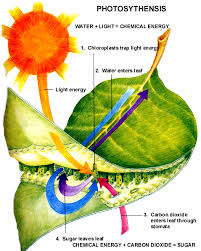
Leaves carry out photosynthesis, which uses carbon dioxide and water to produce sugars and oxygen. They may be single or have many separate leaflets connected by a single stalk. They are shaped to gather the maximum amount of light and contain chlorophyll. Some cells allow the plant to absorb light to carry out photosynthesis, while other cells within the leaf structure regulate the amount of water that is allowed to enter and evaporate from it.
Figure 4: Diagram of a leaf showing its role in photosynthesis.
Interested in biology tutoring services? Learn more about how we are assisting thousands of students each academic year.
SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. We offer tutoring programs for students in K-12, AP classes, and college. To learn more about how we help parents and students in Charlottetown, PE, Canada visit: Tutoring in Charlottetown, PE, Canada