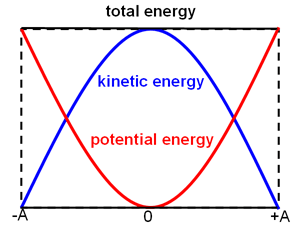
Kinetic and Potential Energy
Energy can take on many forms, two of them being potential and kinetic. Energy is measured in joules (J) which is equivalent to Newton meters (N*m).
Kinetic Energy
Kinetic Energy is the amount of energy an object has due to its motion. This can be represented by the amount of energy of a ball rolling across the floor. The kinetic energy of an object can be calculated using the formula E = ½ mv2 .
E is the kinetic energy in joules.
m is the mass of the object in kilograms.
v is the speed of the object in meters per second.
Example:
Calculate the kinetic energy of a 2kg ball rolling across the floor at a constant speed of 2 m/s.
E = ½ mv2
E = ½ (2)(2)2
E = ½ (2)(4)
E = 4 J
The kinetic energy of the ball is 4 J.
Gravitational Potential Energy
Gravitational Potential Energy is the amount of energy an object possesses due to its position in a gravitational field. This can be represented by holding a ball above your head on the surface of the Earth, where the gravity will be constant. The gravitational potential energy of an object can be calculated using the formula E = mgh.
E is the gravitational potential energy in joules.
m is the mass of the object in kilograms.
g is the acceleration due to of gravity in meters per second squared (on the surface of the Earth, g = 9.81 m/s2) .
h is the height of the object in meters with respect to a reference point (usually the surface of the Earth).
Example:
Calculate the gravitational potential energy of a 2.00kg ball held 3.00m above the surface of the Earth.
E = mgh
E = (2.00)(9.8)(3.00)
E = 58.8 J
The gravitational potential energy of the ball is 58.8J.
Looking to get ready for the SAT? We can help with SAT Prep
This article was written for you by Jeremie, one of the tutors with Test Prep Academy.