Overview
The location of points in a plane can be identified by plotting them as ordered pairs, using the Cartesian coordinate system. It can be determined whether an ordered pair is the solution to a particular equation. The solutions to a linear equation with two variables can be plotted on a graph as a straight line.
Cartesian Coordinate System
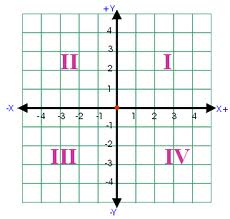
The Cartesian coordinate system is named for the mathematician Rene Descartes, who lived from 1596 to 1650. It was an important discovery because it allowed algebraic equations to be pictured geometrically, and geometric shapes to be defined algebraically. Until that time, algebra and geometry were two separate fields. The Cartesian coordinate system has an x axis (abscissa) and a y axis (ordinate) that are perpendicular to each other. The axes divide the coordinate plane into 4 regions, or quadrants, as shown in the picture below.
Ordered Pairs
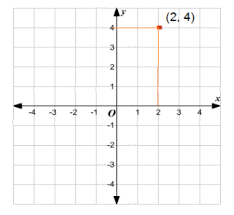
The location of any point on a plane can be described by its coordinates, or ordered pairs. A point in the first quadrant, numbered (I) above, has both x and y coordinates as positive numbers, for example (4, 3). A point in the second quadrant, numbered (II) above, has x coordinates as negative numbers and y coordinates as positive numbers for example (-2, 1). A point in the third quadrant, numbered (III) above, has both x and y coordinates as negative numbers, for example (-2, -2). A point in the fourth quadrant, numbered (IV) above has x coordinates as a positive number and y coordinates as a negative number for example (3 -1). Notice that the origin has the coordinates (0, 0). The axes are not part of the quadrants, so that any time that either the x or y coordinates are on the axis, the value of that coordinate is zero. Notice on the graph below that one point is at the coordinates (2, 4). That means that in order to read its location, it is 2 to the right and 4 up from the x axis.
Graphing Solutions
To see whether or not a particular ordered pair is the solution of an equation with 2 variables, try substituting the values of the ordered pair to see if it solves the equation. If the solution is true, the ordered pair is a solution, but if it is false, the ordered pair is not a solution. For example, is (2, 3) a solution of the equation y = 2x +3? Substitute the 2 for x so that y = 4 +3, or y equals 7. In the ordered pair, y equals 3, so it is not a solution. Is (-2, 4) a solution of 4y – 3x =22. Substitute the -2 for x so that 4y + 6 = 22, so that 4y = 22-6, 4y =16 and y = 4. That statement is true.
Graphing Linear Equations
Linear equations are graphed as straight lines on the Cartesian coordinate system. If the variables are only to the first power, there are no products of variables, and there are no variables in the denominator, then the equation is linear.
Interested in math tutoring services? Learn more about how we are assisting thousands of students each academic year.
SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. We offer tutoring programs for students in K-12, AP classes, and college. To learn more about how we help parents and students in Elko, NV: visit: Tutoring in Elko, NV