Mitosis is a form of cell division that allows a mother cell to give rise to two daughter cells. The daughter cells are genetically identical to each other and to the mother cell. Mitosis involves nuclear division, where the duplicated DNA in the mother cell splits into two identical sets of chromosomes (one set for each daughter cell). Mitosis plays a key part in the repair of biological tissue. There are four main phases in mitosis, which are prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase in this respective order. There is a final stage called cytokinesis, which involves the equal division of cytoplasm between the two daughter cells. An acronym that can be used to remember these phases is PMAT-C.
Prophase
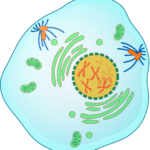 In early prophase, the chromosomes in the cell begin to condense for easy separation in the upcoming stages. The mitotic spindle begins to form and is composed of microtubules called spindle fibers. These fibers grow in between the centrosomes as they move apart to the opposite poles. The spindle fibers are responsible for moving and arranging the chromosomes through the phases. The nucleolus also disappears. When the cell enters late prophase (also known as prometaphase), the chromosomes are completely condensed in their compact sister chromatid forms, the nuclear envelope disintegrates releasing the chromosomes into the cytoplasm, and the mitotic spindle continues to grow while capturing sister chromatids at the kinetochore.
In early prophase, the chromosomes in the cell begin to condense for easy separation in the upcoming stages. The mitotic spindle begins to form and is composed of microtubules called spindle fibers. These fibers grow in between the centrosomes as they move apart to the opposite poles. The spindle fibers are responsible for moving and arranging the chromosomes through the phases. The nucleolus also disappears. When the cell enters late prophase (also known as prometaphase), the chromosomes are completely condensed in their compact sister chromatid forms, the nuclear envelope disintegrates releasing the chromosomes into the cytoplasm, and the mitotic spindle continues to grow while capturing sister chromatids at the kinetochore.
Metaphase
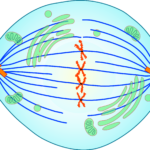 The sister chromatids are aligned at the equatorial/metaphase plate by the spindle fibers. The two kinetochores of the sister chromatids should be attached to spindle fibers from opposite centrosomes.
The sister chromatids are aligned at the equatorial/metaphase plate by the spindle fibers. The two kinetochores of the sister chromatids should be attached to spindle fibers from opposite centrosomes.
Anaphase
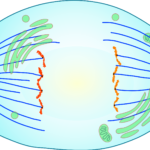 The sister chromatids separate from each other and are pulled to the opposite poles of the cell by the microtubules. The microtubules that are not attached to chromosomes elongate and push apart to lengthen the cell and increase the distance between the poles.
The sister chromatids separate from each other and are pulled to the opposite poles of the cell by the microtubules. The microtubules that are not attached to chromosomes elongate and push apart to lengthen the cell and increase the distance between the poles.
Telophase
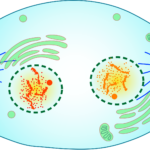 The cell division is almost complete and the structures are starting to be rebuilt in this stage. The mitotic spindle is broken back down into subunits. Two nuclei with a nucleolus and nuclear membrane appear, where there would be one for each daughter cell. The chromosomes decondense and return to being chromatin (the stringy form).
The cell division is almost complete and the structures are starting to be rebuilt in this stage. The mitotic spindle is broken back down into subunits. Two nuclei with a nucleolus and nuclear membrane appear, where there would be one for each daughter cell. The chromosomes decondense and return to being chromatin (the stringy form).
Cytokinesis
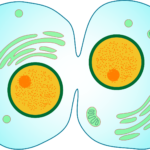 The cytoplasm divides equally into two to form two separate genetically identical daughter cells. In animal cells, cytokinesis involves a pinch in the cell to form a cleavage furrow. This pinch will allow the cell to break and form two cells. In plant cells, a cell plate forms down the middle to form a boundary with cell walls that separate the daughter cells.
The cytoplasm divides equally into two to form two separate genetically identical daughter cells. In animal cells, cytokinesis involves a pinch in the cell to form a cleavage furrow. This pinch will allow the cell to break and form two cells. In plant cells, a cell plate forms down the middle to form a boundary with cell walls that separate the daughter cells.
SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. We offer tutoring programs for students in K-12, AP classes, and college. To learn more about how we help parents and students in Troutdale, Oregon: visit: Tutoring in Troutdale, Oregon.