An adjective is a word, a phrase or a clause used to describe a noun. Adjectives are invariable. They do not change their form depending on the gender or number of the noun. Adjectives describe nouns by answering one of these three questions: What kind is it? How many are there? Which one is it?
Example:
A red tomato Some red tomatoes
To strengthen or emphasise the meaning of an adjective words ‘very’ or ‘really’ are used. An adjective is usually placed in front of a noun or after verbs like ‘to seem’, ‘to look’, ‘to be’ or ‘to taste’.
Examples:
– A black hat
– You look beautiful
– Long road
Types of Adjectives
Following types of adjectives are used most commonly:
1. Adjectives of Number: answer the question ‘how many’
Examples: three, thirty, fifteen
2. Adjectives of Quantity: answer the question ‘how much’
Examples: enough, some, little
3. Adjectives of Quality: answer the question ‘of what kind’
Examples: decent, small, big
4. Demonstrative Adjectives: answer the question ‘which’
Examples: this, that, those
5. Interrogative Adjectives: ask question about a noun
Examples: which, what, where
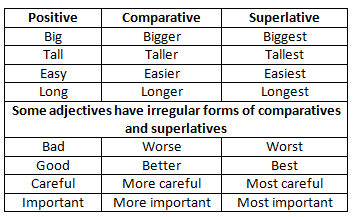
Degrees of Adjectives
Adjectives have three forms: positive, comparative and superlative. Only the comparative and superlative show degree. Comparatives are used to compare two things and the superlatives are used to compare three or more things. the word than frequently accompanies the comparative and the word the precedes the superlative. The inflected suffixes -er and -est suffice to form most comparatives and superlatives, although we need -ier and -iest when a two-syllable adjective ends in y (happier and happiest); otherwise we use more and most when an adjective has more than one syllable.
SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. We offer tutoring programs for students in K-12, AP classes, and college. To learn more about how we help parents and students, visit: SchoolTutoring Academy.