Overview
Chemical equations are shorthand descriptions of the reactions between substances. They include the chemicals that react, the conditions for reaction, the products of the reaction, and the amounts of all substances involved.
Word Equations
In the simplest form, chemical equations can be expressed in words. For example, the substance methane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water. The reactants are methane and oxygen and the products are carbon dioxide and water, such that methane + oxygen → carbon dioxide and water. The arrow pointing to the products of the reaction is another way to say “forms” or “produces.”
Chemical Equations
Although word equations are an improvement over writing a paragraph describing reactions between chemicals, they still lack information, such as the chemical formulas that make up the compounds involved in the reaction and their quantities, their quantities, and details about the reactions themselves. The word methane can be replaced by its chemical formula CH4, oxygen by its molecular state O2, the term carbon dioxide by its chemical formula CO2, and water by its chemical formula H2O. Chemical formulas already state more information than the word forms. A molecule of methane consists of 4 atoms of hydrogen for each atom of carbon; a molecule of carbon dioxide, of two atoms of oxygen for each atom of carbon; a molecule of water, two atoms of hydrogen for each atom of oxygen.
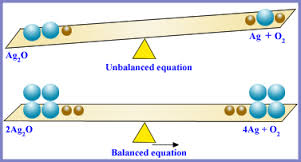
Unbalanced Chemical Equations
After writing a word equation, make sure than the chemical formula for each substance is correct , the reactants are on the left side of the equation, and the products are on the right side of the equation, so that methane + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water becomes CH4 +O2 →CO2 +H2O. The process is not complete. The reactants contain one carbon atom, 4 hydrogen atoms, and two oxygen atoms. The products contain one carbon atom, three oxygen atoms, and two hydrogen atoms.
Balanced Chemical Equations
The Law of Conservation of Mass states that there must be the same amount and type of each substance on both sides of the equation. However, in the unbalanced chemical equation, there are the same number of carbon atoms in CH4 and CO2, but not the same amount of hydrogen and oxygen atoms on both sides of the equation. There are already 4 hydrogen atoms in CH4, so in order to put 4 hydrogen atoms in the products have 2 atoms of H2O. The chemical equation is then CH4 +O2→CO2 +2 H2O. Oxygen is still unbalanced, as there are 2 atoms of oxygen on the reactant side and 4 on the product side. Multiply the O2 by 2 so that the entire reaction is CH4 + 2 O2→ CO2 + 2 H2O. There is one atom of carbon, 4 atoms of hydrogen, and 4 atoms of oxygen on both sides of the chemical equation.
Interested in science tutoring services? Learn more about how we are assisting thousands of students each academic year.
SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. We offer tutoring programs for students in K-12, AP classes, and college. To learn more about how we help parents and students in Greeley, CO: visit Tutoring in Greeley, CO