Overview
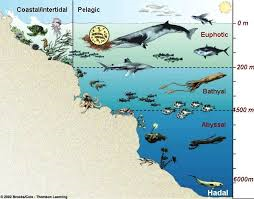
The ocean zones are divided according to their distance from the shore and the depth of the ocean. The area closest to the shore includes the intertidal zone and the coastal ocean. The open ocean is further away from shore and is the largest area. Finally, the deepest parts of the ocean are in the abyssal plain and the ocean trenches.
Ocean Topography
Over 70% of Planet Earth is covered by a vast ocean, usually divided into 5 separate regions; the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Antarctic, and Arctic. Oceanographers usually consider those regions as one vast ocean. In the first 200 meters, the light from the sun penetrates, so photosynthesis can occur in the photic zone. Anything deeper, organisms live and depend upon energy from other sources within the aphotic zone. The continents are surrounded by the continental shelves. The continental slopes are deeper still, and the abyssal plain is the ocean floor, punctuated by deep trenches.
Intertidal Zone and Coastal Oceans
Organisms that live in the intertidal zone have to adapt to extremes to survive. Many of them are submerged at high tide, then exposed at low tide. For example, creatures that live in tide pools, such as various types of sea anemones, sea urchins, barnacles, snails, and seaweed attach firmly to the rocks, so they remain anchored in both conditions. The coastal zones in temperate regions often contain huge forests of kelp seaweed. Those kelp forests nourish the other plants, animals, and fish that dwell within them. Both the intertidal zone and the coastal ocean zone are photic, supporting organisms that require photosynthesis, as well as those who prey on photosynthetic organisms.
Open Ocean
The open ocean begins at the edge of the continental slope, and covers about 90% of the surface of the ocean. The deepest parts of the open ocean are about 4000 meters deep, so some organisms live in the photic part of the open ocean, while others live in the aphotic zones. Most types of saltwater fish live in the open ocean.
Abyssal Plain and Ocean Trenches
The abyssal plain includes the many types of fish and other ocean wildlife that live on the ocean floor, no matter how deep it is. They do not depend upon photosynthesis at all, for the deepest part of the ocean is permanently dark and under great pressure. Organisms below the photic zones rely upon the rain of particles from photosynthetic organisms at the surface, on chemosynthetic processes, feeding upon other organisms, and upon energy from volcanic vents. The deepest ocean trenches are to 11,000 meters. They are not barren, but support a variety of life forms unique to those unusual conditions.
Interested in biology tutoring services? Learn more about how we are assisting thousands of students each academic year.
SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. We offer tutoring programs for students in K-12, AP classes, and college. To learn more about how we help parents and students in Monterey, CA: visit: Tutoring in Monterey, CA