Overview
A direct variation is a linear relationship between variables so they have a constant ratio. It is a special case of the slope-intercept form y =mx +b, where b = 0.
Direct Variation
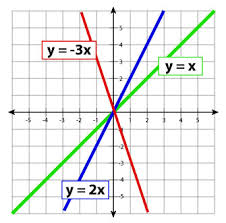
Suppose that Papa’s Pizzeria has a lunch special on pizza, so that one slice sells for $2.00, 2 slices sell for $4.00, 3 slices sell for $6.00 and so on. If the number of slices is represented by x, the cost in dollars is represented by y. The relationship between x and y can be represented by the equation y= 2x. It is a direct variation in the form y=kx, where k is the constant of variation. In this case, the constant of variation equals 2.
Identifying Direct Variation
One of the ways to identify direct variation is to look at the equation and determine if it follows the form. An equation such as y=4x follows the form y=kx, with the constant of variation equaling 4. In order to solve an equation such as -3x +5y =0 for y, first add 3x to both sides, such that -3x +3x +5y = 0 +3x. That leaves the equation 5y=3x. Then both sides can be divided by 5, so that (5y)/5 = (3x)/5. That leaves an equation such as y=3/5x. It is also in the form y=kx, and in this case, the constant of variation equals 3/5. However, an equation such as 2x +y = 10 does not follow the form.
Using Ratios
Another way to look at direct variation is to determine if the ratio y/x is a constant for all values of the variable. Suppose that the ordered pairs include the set {(1, 5) (2, 10) (3, 15) (4, 20)}. The ratio of y/x in the first ordered pair is 5/1. The second pair, 10/2, reduces to 5/1. The third pair, 15/3, also reduces to 5/1, as does the fourth pair, 20/4.
The Slope-Intercept Equation
Any linear equation can be expressed in the form y = mx +b, where m is the slope and b is the intercept. Recall that the slope of a line is the measure of the rate of change, and that any point on the line in a linear relationship will have the same slope. Suppose that the equation is y=2x +1. Two of the ordered pairs on the line have the values (2, 5) and (1, 3). When the line is graphed, the slope is the same at any point on the line.
Interested in math tutoring services? Learn more about how we are assisting thousands of students each academic year.
SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. We offer tutoring programs for students in K-12, AP classes, and college. To learn more about how we help parents and students in Newport, RI: visit: Tutoring in Newport, RI