Overview
According to theories of stellar evolution, most stars spend most of the time converting hydrogen to helium in various nuclear processes. After the supply of hydrogen is exhausted in the stellar core, most stars begin using helium for nuclear fuel. The largest stars use helium as well as other elements for nuclear fusion.
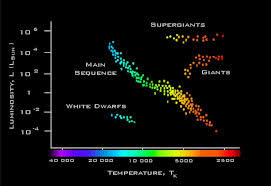
The Main Sequence and Temperature
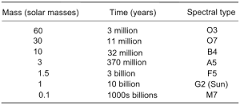
Astronomers Hertzsprung and Russell plotted stars on a graph such that the temperature (or color) of the star was on the x-axis and the absolute magnitude (or brightness) was on the y-axis. They found that most stars were in a band that they called the main sequence. Other astronomers classified the types of stars on the graph. The brightest, hottest stars are called Type O, with a core temperature of almost 40,000 K, then Type B, with a core temperature of around 30,000 K, then Type A, 11,000 K, then Type F, 7200 K, then Type G (like the sun) 5700 K, then Type K, 5240 K, then Type M, about 4000 K.
Stellar Mass
The largest stars on the main sequence are estimated to have a mass of about 40 times the sun, and the smallest stars on the main sequence are about 0.10 times the mass of the sun. Recall that bodies less than 0.08 times the mass of the sun are unable to convert hydrogen to helium with nuclear fusion. The mass of a star is very important in terms of the nuclear fusion reactions that will power it, as well as the time the star is theorized to spend as a main-sequence star. The largest stars burn more brightly and use up their hydrogen fuel more quickly. Because their core temperatures are higher, fusion reactions between other elements can take place that move them off the main sequence.
Supergiants and Red Giants
A star is classified as a supergiant by the type of radiation spectrum it shows, indicating the fusion reactions at its core. Supergiant stars fuse helium and heavier elements, even before they use up the hydrogen in the core. They are less dense and brighter than the main sequence stars. Most of them may explode as supernovae. Some of the most well-known and brightest stars are in these categories: Antares and Arcturus are red supergiants, Rigel is a blue-white supergiant, and Deneb is a white supergiant.
Red Giants
Red giants are classified by their large size and relatively cool temperatures. They may be 10 to hundreds of times as large as the sun, but their density is much lower. Aldebaran and Arcturus are red giants. When the sun uses up its hydrogen in about 5 to 6 billion years, it may become a red giant and swell to the point that it will engulf the orbit of the earth.
Interested in science tutoring services? Learn more about how we are assisting thousands of students each academic year.
SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. We offer tutoring programs for students in K-12, AP classes, and college. To learn more about how we help parents and students in Mishawaka, IN: visit: Tutoring in Mishawaka, IN