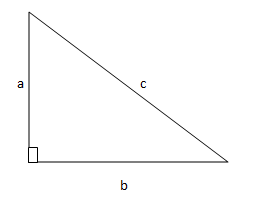
According to Pythagorean Theorem, in a right triangle the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
In the triangle below,
a2 + b2 = c2
– c is the hypotenuse, the longest side
– a and b are the other two sides
To find the hypotenuse, take square root of the sum of squares of the other two sides.
Note: Pythagorean Theorem is applicable only for right angled triangle.