In order for us to complete are daily actions, we need our body to function as a whole. The body does this by having organs work together for different purposes. Our organs are made up of many tissues (sheets of cells) connected together to serve different purposes, to execute actions inside our body and help us get on with our day-to-day lives. Our tissues can be categorized into four major types: Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, and Nervous. Each type of tissue differ from each other in structure which in turn determines its function.
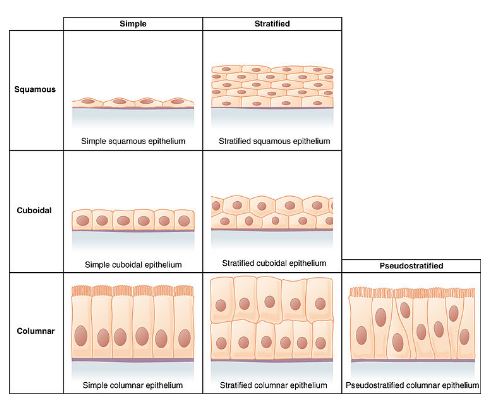
Epithelial tissue serves the main purpose of providing protection for our body’s outer surface and the passageways inside our body. It is found in the lining of our stomach, intestines, trachea, and any other passageways in our body as a form of protection, absorption of nutrients, and secretion of fluids. There are three types of epithelial tissues: squamous, cuboidal, and columnar. Depending on the function of the organ, its epithelial tissue can have varying layers of cells (stratified vs simple). For example, the trachea has pseudostratified columnar epithelial tissue with cilia and mucus to direct movement of any foreign entities whereas the stomach has one layer of columnar epithelial tissue that secretes more mucus to protect the lining from the acid in the stomach.
Connective tissue is the most abundant tissue type in our body. It connects other cells and tissues together. It is typically found in our bones, cartilage, adipose, collagen, blood and many other areas in our body. This shows that connective tissue is very important in providing support and protection in our body. In bones and cartilage, it provides support whereas the collagen in our skin is meant to be elastic and provide protection due to its interlocking matrix.
Muscle
Muscle tissue allows for movement by receiving signals (excitable tissue) to contract our muscles. This results in being able to move our arms, helping with food moving through the digestive system, and allowing our heart to contract. There are three types of muscle tissue in which they each have their own purpose: cardiac, smooth, and skeletal. For example, the heart has cardiac muscle with the specialized purpose of pumping blood throughout the body whereas the stomach has smooth muscle that contracts to help with digestion and movement of food to the intestines.
Nervous tissue conducts and transmits signals (excitable tissue) throughout our body to other muscles and glands. This forms a great way of communication between different organs in the body to maintain homeostasis.There are two types of neural cells in the central and peripheral nervous system: neurons and glia. While neurons transmit impulses to other parts of the body, glial cells may provide protection to the neurons’ axons or help regulate homeostasis.
Interested in science tutoring services? Learn more about how we are assisting thousands of students each academic year.
SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. We offer tutoring programs for students in K-12, AP classes, and college. To learn more about how we help parents and students in Burnaby, British Columbia: visit: Tutoring in Burnaby, British Columbia.