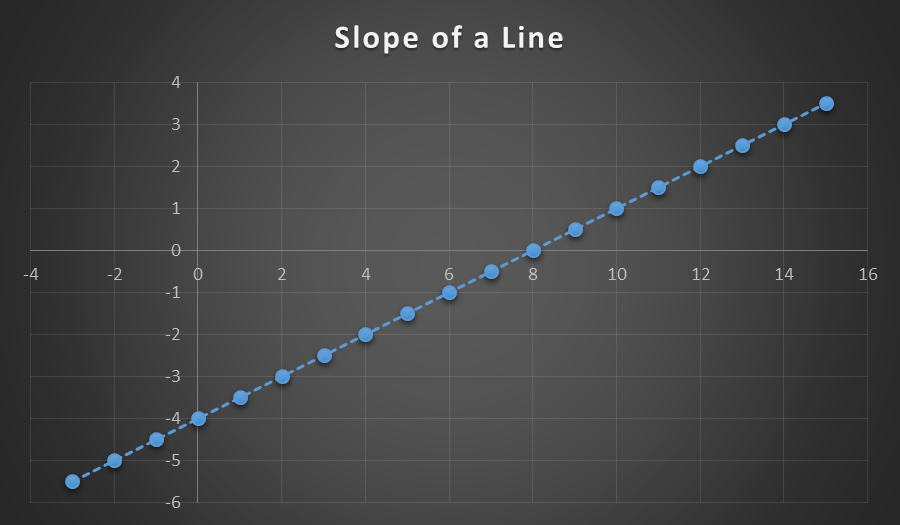
Overview
The slope-intercept equation (y = mx + b) is a linear equation that gives both the slope of a line and where the line crosses the y-axis. It has many applications outside of mathematics, from construction and describing the grade of terrain to describing the results of scientific experiments if there is a linear relationship between the independent and dependent variable.
Slope
The slope of a linear equation is the relationship between the change in the x variable and the change in the y variable. It is a ratio, defined as the change in y (the rise) over the change in x (the run). In symbol form, the slope of a line containing the points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) equals the ratio of (y2-y1)/(x2-x1). When solving a linear equation, the y coordinates must be subtracted in the same order as the x coordinates in order to solve the equation, and describe the line correctly. Suppose a line contains the points (1, 2) and (4, 4). The slope will equal the ratio of (4-2)/ (4-1) or 2/3.
Figure 1: The slope of a line is a ratio of the change in y (the rise) over the change in x (the run).
Direction of a Line
The slope of a line also tells how it slants. Suppose that m is positive, such as in the previous example of 2/3. The line slants upwards from left to right. If m is negative, the line slants downward from left to right. The larger the slant, the greater the slope. If the line is parallel to the x-axis, the slope is 0. A line that is parallel to the y axis, however, has an undefined slope, as it is like dividing by zero.
Figure 2: If there is no change in y, the slope of the line is 0, and the line is parallel to the x axis.
Y-Intercept
The y-intercept is the point where the line crosses the y-axis. Recall in a graph of Cartesian coordinates there is an x-axis (the horizontal one) and a y-axis (the vertical one). In a linear equation, the y-intercept is a single point, a constant.
Figure 3: The y intercept is a single point, a constant
Applications of the Slope-Intercept Equation
Suppose that a hill has a grade of 10%. That is the rise over the run, or for every horizontal distance of 100 feet the road rises 10 feet. Snoqualmie Pass is the largest pass in Washington State that is kept open year-round, and a major east-west route over I-90. A route from Seattle to the summit of Snoqualmie pass goes from an elevation of 520 feet to elevation of 3022 feet, a rise of approximately 2502 feet. Although the distance between Seattle and Snoqualmie pass is about 50 miles, the grade varies and frequently exceeds the recommended average grade of 6% for interstate highways. This makes it more difficult for long-distance truckers carrying heavy loads between the eastern and western parts of the state, so that highway engineers are constantly modifying the highway to improve conditions.
Figure 4: Snoqualmie Pass is a major route over I-90, and is kept open year-round as road conditions allow.
Interested in algebra tutoring services? Learn more about how we are assisting thousands of students each academic year.
SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. We offer tutoring programs for students in K-12, AP classes, and college. To learn more about how we help parents and students in Issaquah, WA: visit Tutoring in Issaquah, WA